Publication of the report “ To Err is Human ” was associated with an increased number of patient safety publications and research awards. The report appears to have stimulated research and discussion about patient safety issues, but whether this will translate into safer patient care remains unknown. Keywords: medical literature, patient safety
What overall message was stated by the Institute of Medicine report To Err Is Human?
The message in To Err is Human was that preventing death and injury from medical errors requires dramatic, systemwide changes.
What is the point of err is human?
The Institute of Medicine's To Err Is Human1 was transformational for patient safety. It brought the problem of medical errors into the public eye and highlighted why every health care organization in the US must consider safety as a priority.
What is an error in patient safety?
Error. An action or omission that entails deviating from the plan, following a wrong plan, or no plan. Whether harm arises from this is irrelevant for the definition of an error. Near miss. An error without harm that could have resulted in harm.
What was the government's response to the Harvard report To Err Is Human?
As a result of the report President Bill Clinton signed Senate bill 580, the Healthcare Research and Quality Act of 1999, which renamed The Agency for Health Care Policy and Research to Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality to indicate a change in focus. The bill also funded projects through that organization.
What are the focus areas of the To Err is Human recommendations?
What are the 4 focus areas of recommendations made by "To Err is Human" to decrease Human errors by 50% in 5 years:Enhance knowledge and leadership regarding safety.Identify and learn from errors.Set performance standards and expectations for safety.Implement safety systems within health-care organizations.
How do you cite to err is human building safer health system?
Suggested Citation Institute of Medicine. 2000. To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Health System. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
What are 2 common medical errors related to patient safety?
Misdiagnosis, falls, infections, mistakes during treatment and getting the wrong medication are the most common PSIs experienced.
What is the process for reporting errors in patient care?
There are several steps to appropriately dealing with a medical error that are relatively straightforward:Let the patient and family know. ... Notify the rest of the care team. ... Document the error and report it to the hospital safety committee.
What are the top 5 medical errors?
The top five medical errors are misdiagnosis, delayed diagnosis, medication error, infection, and harmful medical devices. The top five medical errors are responsible for most instances of medical malpractice in health care.
How does Npsg improve healthcare?
The National Patient Safety goals aspire to reduce HAPIs by having care providers assess and periodically reassess each resident patient's risk for developing a pressure ulcer, as well taking any further action necessary to address any identified risks.
What report first sparked the current patient safety movement?
report To Err Is HumanThe IOM's 1999 report To Err Is Human was one of the first to herald the culture of safety in the U.S. healthcare system.
Who was the first known person to use the term preventable harm in healthcare?
[MUSIC] Welcome back everybody, the term preventable harm was first used during the Crimean War in the mid 1800s. A nurse by the name of Florence Nightingale found poor care for wounded soldiers.
What does it mean to err is human to forgive divine?
idiom saying. something that you say that means that it is natural for people to make mistakes and it is important to forgive people when they do. SMART Vocabulary: related words and phrases.
Who said to err is human to forgive?
Alexander Pope12) “To err is human, to forgive, divine.” – Alexander Pope.
Are humans forgive divine?
Despite our best efforts, we are all fallible and make mistakes. Some of these mistakes are trivial, while others are serious, and even fatal.
What do we mean by a just culture?
“Just Culture” refers to a system of shared accountability in which organizations are accountable for the systems they have designed and for responding to the behaviors of their employees in a fair and just manner.
When was the report "To Err is Human" published?
Background: The “ To Err is Human ” report published by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) in 1999 called for a national effort to make health care safer. Although the report has been widely credited with spawning efforts to study and improve safety in health care, there has been limited objective assessment of its impact. We evaluated the effects of the IOM report on patient safety publications and research awards.
What is the conclusion of the report "To Err is Human"?
Conclusions: Publication of the report “ To Err is Human ” was associated with an increased number of patient safety publications and research awards. The report appears to have stimulated research and discussion about patient safety issues, but whether this will translate into safer patient care remains unknown.
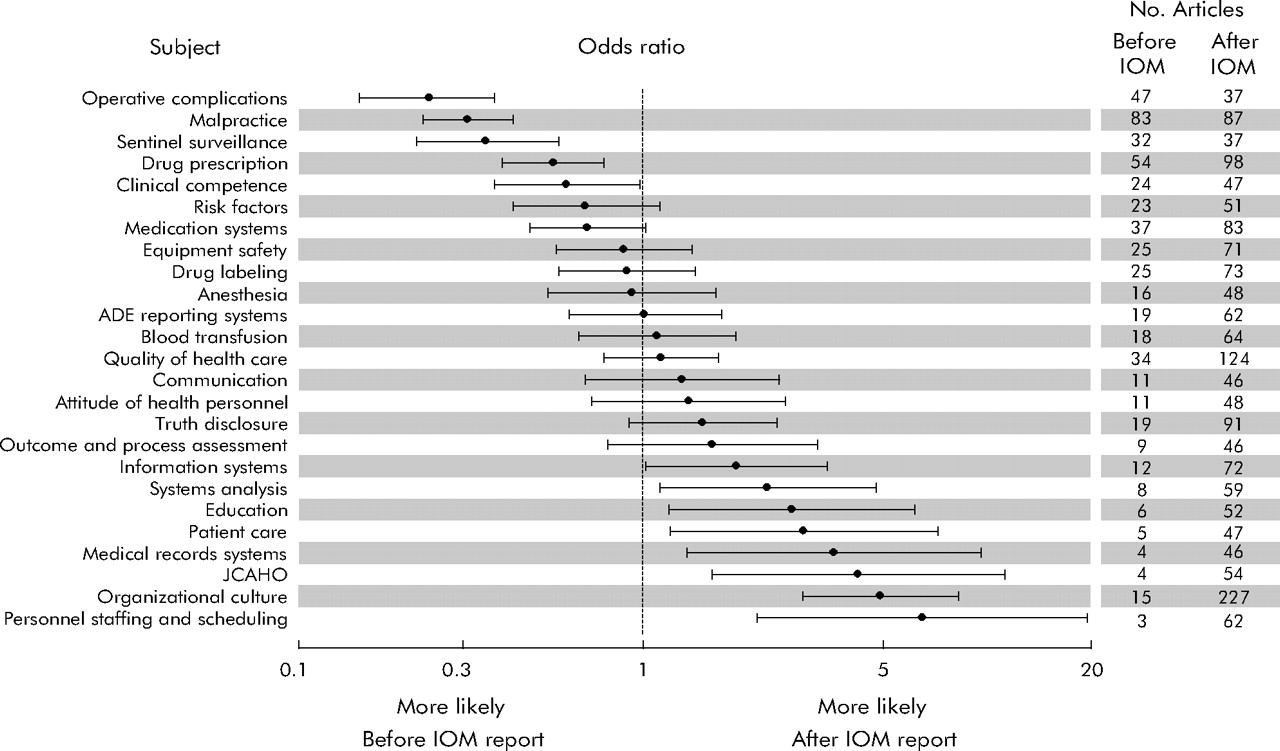
What is the principal subject of patient safety publications before and after publication of the IOM report?
Principal subject of patient safety publications before and after publication of the IOM report “ To Err is Human ”.
How many articles were in MEDLINE in 2005?
The literature search identified 12 429 articles from among 5 207 194 MEDLINE publications between 1 January 1994 and 1 January 2005. Thirteen duplicates were identified leaving 12 416 publications for review. Patient safety or medical errors were identified as the principal focus for 5905 publications (48%). Six articles were excluded because the date of publication could not be identified. Among the remaining articles, 5514 were published between 1 November 1994 and 1 November 2004 in 1095 journals from 40 countries and were included in the principal analyses. The search of the CRISP database identified 1745 awards out of 732 826 federally funded research awards granted for the fiscal years 1995–2004. Patient safety or medical errors were identified as the principal focus for 567 (32%) of the research awards. Agreement on the classification of publications and research awards was good: principal publication focus on patient safety or medical errors (agreement 86%, κ = 0.71), publication type (agreement 74%, κ = 0.67), publication subject (agreement 60%, κ = 0.57), methodology of reports of original research (agreement 68%, κ = 0.58), and principal research award focus on patient safety or medical errors (agreement 90%, κ = 0.77).
Why is "to error is human" important?
“ To Err is Human ” has provided a window of opportunity for improving patient safety in health care.
When was MEDLINE used to identify articles on patient safety and medical errors?
Methods: We searched MEDLINE to identify English language articles on patient safety and medical errors published between 1 November 1994 and 1 November 2004. Using interrupted time series analyses, changes in the number, type, and subject matter of patient safety publications were measured. We also examined federal (US only) funding of patient safety research awards for the fiscal years 1995–2004.
When was the IOM report published?
Publications were aggregated into 3 month intervals and data analysis was limited to the 5 year periods before (1 November 1994 to 1 November 1999) and after (1 November 1999 to 1 November 2004) the 1 November 1999 release of the IOM report. Patient safety research awards were analyzed in yearly intervals to coincide with funding decisions for each fiscal year (1 October to 30 September). Data analysis was limited to the five fiscal year periods before (1995–1999) and after (2000–2004) the release of the IOM report.
Author information
1. Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
Abstract
The "To Err is Human" report published by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) in 1999 called for a national effort to make health care safer. Although the report has been widely credited with spawning efforts to study and improve safety in health care, there has been limited objective assessment of its impact.
Abstract
The “ To Err is Human ” report published by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) in 1999 called for a national effort to make health care safer. Although the report has been widely credited with spawning efforts to study and improve safety in health care, there has been limited objective assessment of its impact.
Methods
Using data from a period of 10 years, we evaluated changes in patient safety publications in MEDLINE indexed journals and federal research funding associated with the release of the IOM report “ To Err is Human ”.
Results
The literature search identified 12 429 articles from among 5 207 194 MEDLINE publications between 1 January 1994 and 1 January 2005. Thirteen duplicates were identified leaving 12 416 publications for review. Patient safety or medical errors were identified as the principal focus for 5905 publications (48%).
Discussion
We have examined the impact of the IOM report “ To Err Is Human ” on the health sciences literature and found a substantial increase in the number of patient safety publications and research awards following the release of the report. Increased rates of publication were observed for all types of patient safety articles.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Carole Foxman for database searches; Ralph Gertler and Joseph Meltzer for publication and research award reviews; and David Blumenthal, Clifford Deutschman, and Donald Redelmeier for their comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
When was the report "To Err is Human" released?
On November 29, 1999 , the Institute of Medicine (IOM) released a report called To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System.1The IOM released the report before the intended date because it had been leaked, and one of the major news networks was planning to run a story on the evening news.2Media throughout the country recognized this opportunity for a headline story describing a very large number of hospital deaths from medical errors —possibly as great as 98,000 per year. The problem in other care settings was unknown, but suspected to be great.
What is the message of "To Err is Human"?
Errors occur in health care as well as every other very complex system that involves human beings. The message in To Err is Humanwas that preventing death and injury from medical errors requires dramatic, systemwide changes.1Among three important strategies—preventing, recognizing, and mitigating harm from error—the first strategy (recognizing and implementing actions to preventerror) has the greatest potential effect, just as in preventive public health efforts.
What is chapter 3 of To Err is Human?
Chapter 3An Overview of To Err is Human: Re-emphasizing the Message of Patient Safety
How to prevent errors in clinical practice?
Some actions are clinically oriented and evidence-based: communicating clearly to other team members, even when hierarchies and authority gradients seem to discourage it; requesting and giving feedback for all verbal orders; and being alert to “accidents waiting to happen.” Other opportunities are broader in focus or address the work environment and may require clinical leadership and changing the workplace culture: simplifying processes to reduce handoffs and standardizing protocols; developing and participating in multidisciplinary team training; involving patients in their care; and being receptive to discussions about errors and near misses by paying respectful attention when any member of the staff challenges the safety of a plan or a process of care.
What is NCBI bookshelf?
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
How to reduce the likelihood of error?
Simplify key processes. Simplifying key processes can minimize problem-solving and greatly reduce the likelihood of error. Simplifying includes reducing the number of steps or handoffs that are needed. Examples of processes that can usually be simplified are writing an order, then transcribing and entering it in a computer, or having several people record and enter the same data in different databases. Other examples of simplification include limiting the choice of drugs and dose strengths available in the pharmacy, maintaining an inventory of frequently prepared drugs, reducing the number of times a day a drug is administered, keeping a single medication administration record, automating dispensing, and purchasing equipment that is easy to use and maintain.
Why is health care prone to errors?
Partly because of its sheer complexity and the number of different individuals with different training and approaches, health care is prone to harm from errors—especially in operating rooms, intensive care units (ICUs), and emergency departments where there is little time to react to unexpected events—and consequences can be very serious.
How does incident reporting improve patient safety?
Incident reporting in health care prevents error recurrence , ultimately improving patient safety. A qualitative systematic review was conducted, aiming to identify barriers to incident reporting among nurses. Joanna Briggs Institute methodology for qualitative systematic reviews was followed, with data extracted using JBI QARI tools, and selected studies assessed for methodological quality using Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP). A meta-aggregation synthesis was carried out, and confidence in findings was assessed using GRADE ConQual. A total of 921 records were identified, but only five studies were included. The overall methodological quality of these studies was good and GRADE ConQual assessment score was “moderate.” Fear of negative consequences was the most cited barrier to nursing incident reporting. Barriers also included inadequate incident reporting systems and lack of interdisciplinary and interdepartmental cooperation. Lack of nurses’ necessary training made it more difficult to understand the importance of incident reporting and the definition of error. Lack of effective feedback and motivation and a pervasive blame culture were also identified.
What is CRM in emergency medicine?
Between 60 and 70% of all errors in high-risk areas—such as medicine—are assigned to the field of “human factors”. In aviation, after several aircraft disasters, the concept of “Crew Resource Management” (CRM) was developed in the 1980s to avoid such errors and has since established itself in many high-security industries. In contrast to medicine, there has long been a legal obligation in aviation to conduct regular CRM training. Introduced into medicine by anesthesiologists in 1990 because of its potential, CRM training has so far found its way into emergency medicine especially, even without it being a legal obligation. For trauma room treatment of polytrauma patients, the disciplines involved already offer a specially developed training concept in which teaching of CRM principles is the main focus (HOTT®-Schockraumsimulation). In addition to dedicated private providers of CRM training and individual concepts developed at an institutional level, several common course concepts for the care of emergency patients also integrate CRM principles to varying degrees into their curricula and teaching methods. Level IA evidence for CRM training is still missing also due to systematic difficulties not only in medicine, but also in other high-risk areas. However, further implementation of regular CRM training in medicine should not be suspended for this very reason.
What is a general statistical methodology for the analysis of multivariate categorical data arising from observer reliability?
The procedure essentially involves the construction of functions of the observed proportions which are directed at the extent to which the observers agree among themselves and the construction of test statistics for hypotheses involving these functions. Tests for interobserver bias are presented in terms of first-order marginal homogeneity and measures of interobserver agreement are developed as generalized kappa-type statistics. These procedures are illustrated with a clinical diagnosis example from the epidemiological literature.
Is there an objective assessment of the impact of safety in health care?
efforts to study and improve safety in health care, there has been limited objective assessment of its impact.