Documentation of a basic, normal neuro exam should look something along the lines of the following: The patient is alert and oriented to person, place, and time with normal speech. No motor deficits are noted, with muscle strength 5/5 bilaterally.
Full Answer
Which cranial nerves are usually evaluated during the examination of the eyes?
During a complete neurological exam, most of these nerves are evaluated to help determine the functioning of the brain: Cranial nerve I (olfactory nerve). This is the nerve of smell. The patient may be asked to identify different smells with his or her eyes closed. Cranial nerve II (optic nerve).
How to conduct a cranial nerve examination?
To assess the corneal reflex:
- Clearly explain what the procedure will involve to the patient and gain consent to proceed.
- Gently touch the edge of the cornea using a wisp of cotton wool.
- In healthy individuals, you should observe both direct and consensual blinking. The absence of a blinking response suggests pathology involving either the trigeminal or facial nerve.
How does a nurse assess cranial nerve function?
assessment technique. Motor: Ask patient to frown, smile, and wrinkle brow. Inability or asymmetrical facial expression is positive for CN VII lesion. Cranial Nerve VIII (Vestibulocochlear Nerve): Sensory for hearing, motor for balance Vestibular branch (balance): Ask patient to march in place (Mittlemeyer Marching) with eyes closed.
What cranial nerve is not attached to brainstem?
The olfactory nerve, or cranial nerve I, is the first of the 12 cranial nerves. It is instrumental in the sense of smell. The olfactory nerve is the shortest of the 12 cranial nerves and only one of two cranial nerves (the other being the optic nerve) that do not join with the brainstem.

How do you document the normal cranial nerve assessment?
Documentation of a basic, normal neuro exam should look something along the lines of the following: The patient is alert and oriented to person, place, and time with normal speech. No motor deficits are noted, with muscle strength 5/5 bilaterally. Sensation is intact bilaterally.
What is a 12 cranial nerve assessment?
The 12th (hypoglossal) cranial nerve is evaluated by asking the patient to extend the tongue and inspecting it for atrophy, fasciculations, and weakness (deviation is toward the side of a lesion).
What does the cranial nerve examination indicate?
The cranial nerve examination may reveal signs of sensory or motor dysfunction that could affect gait. Decreased visual acuity, visual field deficits, or visual neglect may cause a patient to adopt a cautious gait pattern and may contribute to falls.
How do you check cranial nerves in nursing?
Cranial Nerve III, IV, and VI – Oculomotor, Trochlear, AbducensTest eye movement by using a penlight. Stand 1 foot in front of the patient and ask them to follow the direction of the penlight with only their eyes. ... Test bilateral pupils to ensure they are equally round and reactive to light and accommodation .
How do you test cranial nerve 7?
1:162:51Cranial Nerve 7 | Facial Nerve Assessment for PhysiotherapistsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAsk the patient to close the eyes tightly. While you try to force them. Open muscles in the lowerMoreAsk the patient to close the eyes tightly. While you try to force them. Open muscles in the lower half of the face can be tested by asking the patient to show their teeth smile or puff out the cheeks.
How do you check cranial nerve 9?
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX) The glossopharyngeal nerve provides sensory supply to the palate. It can be tested with the gag reflex by touching the pharynx with a tongue depressor or by touching the arches of the pharynx.
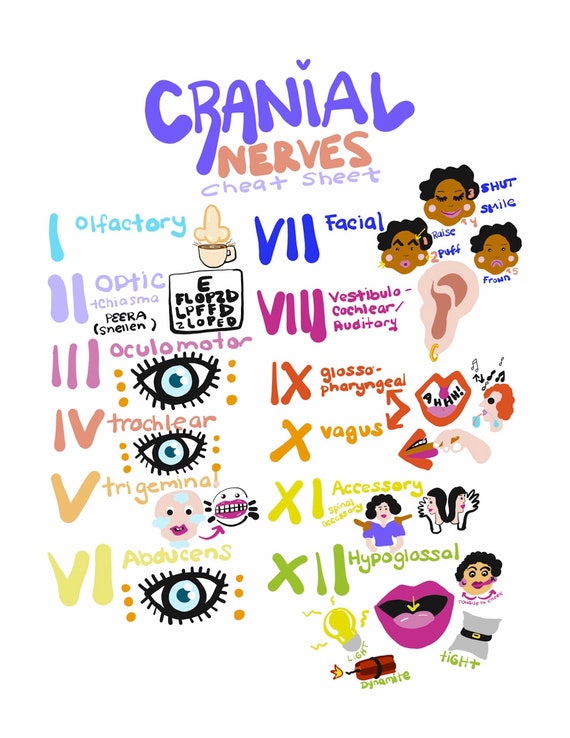
What are the 12 cranial nerves names?
In higher vertebrates (reptiles, birds, mammals) there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves: olfactory (CN I), optic (CN II), oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), trigeminal (CN V), abducent (or abducens; CN VI), facial (CN VII), vestibulocochlear (CN VIII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X), accessory (CN XI), and ...
What do the 12 cranial nerves control?
The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your brain. Cranial nerves send electrical signals between your brain, face, neck and torso. Your cranial nerves help you taste, smell, hear and feel sensations. They also help you make facial expressions, blink your eyes and move your tongue.
What are the 4 components of a neurological check?
The neurologic examination is typically divided into eight components: mental status; skull, spine and meninges; cranial nerves; motor examination; sensory examination; coordination; reflexes; and gait and station. The mental status is an extremely important part of the neurologic examination that is often overlooked.
What is the 7 cranial nerve?
The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve (CN VII). It arises from the brain stem and extends posteriorly to the abducens nerve and anteriorly to the vestibulocochlear nerve.
How do you check cranial nerve 5?
1:413:03Cranial Nerve 5 | Trigeminal Nerve Assessment for PhysiotherapistsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAsk the patient to gaze into the distance. Then using a wisp of cotton touch the cornea gently.MoreAsk the patient to gaze into the distance. Then using a wisp of cotton touch the cornea gently. Observe for a blinking reflex in both eyes and ask the patient if they felt the touch.
How do you test cranial nerve 10?
The gag reflex tests both the sensory and motor components of CN 9 & 10. This involuntary reflex is obtained by touching the back of the pharynx with the tongue depressor and watching the elevation of the palate.
What do the 12 cranial nerves control?
The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your brain. Cranial nerves send electrical signals between your brain, face, neck and torso. Your cranial nerves help you taste, smell, hear and feel sensations. They also help you make facial expressions, blink your eyes and move your tongue.
What are the 12 cranial nerves Mnemonic?
Remembering cranial nerve names in order of CN I to CN XII: On old Olympus's towering top a Finn and German viewed some hops. Ooh, ooh, ooh to touch and feel very good velvet. Such heaven!
How do you assess the hypoglossal nerve?
The hypoglossal nerve can be examined by asking a patient to protrude their tongue, move their tongue laterally, and place their tongue against their cheek to resist the opposing force of the examiner's hand resting on the external cheek.
What are the 12 cranial nerves names?
In higher vertebrates (reptiles, birds, mammals) there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves: olfactory (CN I), optic (CN II), oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), trigeminal (CN V), abducent (or abducens; CN VI), facial (CN VII), vestibulocochlear (CN VIII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X), accessory (CN XI), and ...
How many cranial nerves are there?
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves although the optic nerve is really an extension of the brain rather than a peripheral nerve. The ability to test them swiftly, efficiently and to interpret the findings should be a core competency for general practice.
How to test nerves?
The nerves are tested by having bottles containing characteristic substances such as peppermint, coffee or lavender and asking the patient to identify each in turn. If you do not have such tools available, ask the patient to close his/her eyes and then hold a bar of soap under the patient's nose for them to smell.
Why do neurologists omit the corneal reflex?
Many neurologists omit the corneal reflex unless a sensory deficit is found , especially in the ophthalmic division , or if there is a lesion of another cranial nerve. Take a clean piece of cotton wool and ask the patient to look away from the side being tested. Gently touch the cornea with the cotton wool and the patient will blink. This requires the sensation of V but also the motor of VII.
How to test olfactory nerve?
Testing the olfactory nerve is often omitted. Before starting, check that there is free flow of air by occluding each nostril in turn and asking the patient to sniff in. The nerves are tested by having bottles containing characteristic substances such as peppermint, coffee or lavender and asking the patient to identify each in turn. If you do not have such tools available, ask the patient to close his/her eyes and then hold a bar of soap under the patient's nose for them to smell.
Which nerves are responsible for controlling the external ocular muscles?
These three nerves are examined together, as they control the external ocular muscles. The oculomotor nerve supplies the internal muscles of the eye including sympathetic fibres to dilate the pupil and parasympathetic fibres to constrict it and to reduce the focal length of the lens for accommodation.
Which nerve supplies the trapezius and sternomastoid muscles?
The accessory nerve supplies the trapezius and sternomastoid muscles. Is there any wasting? Ask the patient to shrug his/her shoulders up and try to push them down. Ask the patient to push his/her head forwards against your hand. Both these movements should be very difficult to resist.
What are the two important aspects of the optic nerve?
Two important aspects of the optic nerve are visual acuity and visual field.
How many cranial nerves are there?
Listed below is a chart of the 12 cranial nerves, the assessment technique used, if the response elicited is normal, and how to document it.
How many cranial nerves are there in the nervous system?
Assessment of the cranial nerves provides insightful and vital information about the patient’s nervous system. There are 12 cranial nerves that are often forgotten by nurses, so with that in mind, here’s a free assessment form that you can use!
What reflex should a client have to respond to light and deep sensation?
While the client looks upward, lightly touch the lateral sclera of eye to elicit blink reflex. Client should have a (+) corneal reflex, able to respond to light and deep sensation and able to differentiate hot from cold. Client was able to elicit corneal reflex, sensitive to pain stimuli and distinguish hot from cold.
How to test light sensation?
(same as above) (same as above) To test deep sensation, use alternating blunt and sharp ends of an object. Determine sensation to warm and cold object by asking client to identify warmth and coldness. (same as above)
What is the purpose of cranial nerve exam?from en.wikipedia.org
The cranial nerve exam is a type of neurological examination. It is used to identify problems with the cranial nerves by physical examination. It has nine components. Each test is designed to assess the status of one or more of the twelve cranial nerves (I-XII).
Which nerve is used to perform the Corneal Reflex test?from en.wikipedia.org
Corneal reflex is conducted along with the facial nerve section of the test. Note the sensory innervation of the cornea is provided by the trigeminal nerve while the motor innervation for blinking the eye is provided by the facial nerve .-. Muscles of mastication ( temporalis, masseter) should be inspected for atrophy.
How many efferent limbs are there in the pupillary reflex?from geekymedics.com
Each afferent limb of the pupillary reflex has two efferent limbs, one ipsilateral and one contralateral. The afferent limb functions as follows: Sensory input (e.g. light being shone into the eye) is transmitted from the retina, along the optic nerve to the ipsilateral pretectal nucleus in the midbrain.
What is the name of the muscle that innervates the trochlear nerve?from geekymedics.com
Trochlear nerve palsy (CN IV) The only muscle the trochlear nerve innervates is the superior oblique muscle . As a result, trochlear nerve palsy (‘fourth nerve palsy’) typically results in vertical diplopia when looking inferiorly, due to loss of the superior oblique’s action of pulling the eye downwards.
Which nerves transmit motor information to the extraocular muscles to control eye movement and eyelid function?from geekymedics.com
The oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV) and abducens (CN VI) nerves transmit motor information to the extraocular muscles to control eye movement and eyelid function. The oculomotor nerve also carries parasympathetic fibres responsible for pupillary constriction.
What is visual neglect?from geekymedics.com
Visual neglect (also known as visual inattention) is a condition in which an individual develops a deficit in their awareness of one side of their visual field. This typically occurs in the context of parietal lobe injury after stroke, which results in an inability to perceive or process stimuli on one side of the body. The side of the visual field that is affected is contralateral to the location of the parietal lesion. It should be noted that visual neglect is not caused by optic nerve pathology and therefore this test is often not included in a cranial nerve exam.
What causes facial nerve palsy?from geekymedics.com
Facial nerve palsy presents with unilateral weakness of the muscles of facial expression and can be caused by both upper and lower motor neuron lesions.
What nerves are used to test for symmetry of movement?
For the 3rd (ocolomotor), 4th (trochlear), and 6th (abducens) cranial nerves , eyes are observed for symmetry of movement, globe position, asymmetry or droop of the eyelids (ptosis), and twitches or flutters of globes or lids. Extraocular movements controlled by these nerves are tested by asking the patient to follow a moving target (eg, examiner’s finger, penlight) to all 4 quadrants (including across the midline) and toward the tip of the nose; this test can detect nystagmus and palsies of ocular muscles. Brief fine amplitude nystagmus at end-lateral gaze is normal.
How to test trigeminal nerve?
For the 5th (trigeminal) nerve, the 3 sensory divisions (ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular) are evaluated by using a pinprick to test facial sensation and by brushing a wisp of cotton against the lower or lateral cornea to evaluate the corneal reflex. If facial sensation is lost, the angle of the jaw should be examined; sparing of this area (innervated by spinal root C2) suggests a trigeminal deficit. A weak blink due to facial weakness (eg, 7th cranial nerve paralysis) should be distinguished from depressed or absent corneal sensation, which is common in contact lens wearers. A patient with facial weakness feels the cotton wisp normally on both sides, even though blink is decreased.
What nerve is evaluated for hemifacial weakness?
The 7th (facial) cranial nerve is evaluated by checking for hemifacial weakness. Asymmetry of facial movements is often more obvious during spontaneous conversation, especially when the patient smiles or, if obtunded, grimaces at a noxious stimulus; on the weakened side, the nasolabial fold is depressed and the palpebral fissure is widened. If the patient has only lower facial weakness (ie, furrowing of the forehead and eye closure are preserved), etiology of 7th nerve weakness is central rather than peripheral.
What is the 2nd cranial nerve?
For the 2nd (optic) cranial nerve, visual acuity is tested using a Snellen chart for distance vision or a handheld chart for near vision; each eye is assessed individually , with the other eye covered.
What is the function of the 1st cranial nerve?
Smell, a function of the 1st (olfactory) cranial nerve, is usually evaluated only after head trauma or when lesions of the anterior fossa (eg, meningioma) are suspected or patients report abnormal smell or taste.
What type of plate is used to test color perception?
Color perception is tested using standard pseudoisochromatic Ishihara or Hardy-Rand-Ritter plates that have numbers or figures embedded in a field of specifically colored dots.
Which cranial nerve carries vestibular and auditory input?
Because the 8th (vestibulocochlear, acoustic, auditory) cranial nerve carries auditory and vestibular input, evaluation involves
What is a neurological exam?
The neurological exam consists of a number of components that assess for neurological abnormalities. The level of detail of the neurological exam performed in the clinical setting varies with each patient depending on history and symptoms. Patients presenting with neurological deficits, or symptoms of neurological conditions, for example, ...
What is neuro exam?
A neuro exam is one of the more complex body systems to master when it comes to assessment and documentation. Testing the cranial nerves, for example, takes practice. Omitting a small part of the process can mean missing a potentially serious diagnosis.
What is the mental status of a patient?
Mental Status: The patient is alert and oriented to person, place, and time with normal speech. Memory is normal and thought process is intact.
Is Sensation intact bilaterally?
Sensation: Sensation is intact bilaterally to pain and light touch. Two-point discrimination is intact.
Do you need a neurological assessment?
Patients presenting with neurological deficits, or symptoms of neurological conditions, for example, may require a complete neurological assessment. Patients presenting for non-neurological complaints may only require a simple assessment of mental status.
What is the purpose of cranial nerve exam?
The cranial nerve exam is a type of neurological examination. It is used to identify problems with the cranial nerves by physical examination. It has nine components. Each test is designed to assess the status of one or more of the twelve cranial nerves (I-XII).
Which nerve is used to perform the Corneal Reflex test?
Corneal reflex is conducted along with the facial nerve section of the test. Note the sensory innervation of the cornea is provided by the trigeminal nerve while the motor innervation for blinking the eye is provided by the facial nerve .-. Muscles of mastication ( temporalis, masseter) should be inspected for atrophy.
How is extraocular movement measured?
Extraocular movements is tested by inspecting for ptosis, eye position and nystagmus. The pupil size is measured, its shape and any asymmetry is tested. A commonly used abbreviation to describe normal pupils is PERRLA (pupils equal, round and reactive to light and accommodation).
How to test hearing?
Hearing is tested by whispering numbers in one ear as patient covers the other and ask the patient to repeat the numbers. Alternatively, have patient close their eyes and say "left" or "right" depending on the side from which they hear the sound. Vigorously rub fingers together in one ear at a time to produce rustling sound. Conduct the Rinne test and Weber test.
How are visual fields assessed?
Visual fields are assessed by asking the patient to cover one eye while the examiner tests the opposite eye. The examiner wiggles the finger in each of the four quadrants and asks the patient to state when the finger is seen in the periphery.
What nerve innervates the mandible?
Be careful not to test the mandibular division too laterally, as the mandible is innervated by the great auricular nerve (C2 and C3). A common mistake is to use a stroking motion, which will trigger pain and temperature nerves. Instead, a point stimulus should be applied.
What nerve is used to test smell?
I: Olfactory nerve. Sense of smell. Smell is tested in each nostril separately by placing stimuli under one nostril and occluding the opposing nostril. The stimuli used should be non-irritating and identifiable. Some example stimuli include cinnamon, cloves, and toothpaste.
Which side of the face is affected by LMN?
Note forehead and lower face are affected on the right, which is same side of the LMN lesion Note forehead sparing on right side, opposite the UMN lesion
Can CN 7 dysfunction show bilaterally?
Central (i.e. UMN) CN 7 dysfunction (e.g. stroke) - not shown: Can wrinkle forehead bilaterally; will demonstrate loss of lower facial movement on side opposite stroke.
What is done during a neurological exam?from hopkinsmedicine.org
During a neurological exam, the healthcare provider will test the functioning of the nervous system. The nervous system is very complex and controls many parts of the body. The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, 12 nerves that come from the brain, and the nerves that come from the spinal cord. The circulation to the brain, arising from the arteries in the neck, is also frequently examined. In infants and younger children, a neurological exam includes the measurement of the head circumference. The following is an overview of some of the areas that may be tested and evaluated during a neurological exam:
What is neurology exam?from hopkinsmedicine.org
A neurological exam, also called a neuro exam, is an evaluation of a person's nervous system that can be done in the healthcare provider's office. It may be done with instruments, such as lights and reflex hammers. It usually does not cause any pain to the patient. The nervous system consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and the nerves from these areas. There are many aspects of this exam, including an assessment of motor and sensory skills, balance and coordination, mental status (the patient's level of awareness and interaction with the environment), reflexes, and functioning of the nerves. The extent of the exam depends on many factors, including the initial problem that the patient is experiencing, the age of the patient, and the condition of the patient.
How to test bicep reflex?from oxfordmedicaleducation.com
To test the biceps reflex ask the patient to place their hands on their abdomen and let their arms relax. Place a finger over the biceps tendon in the antecubital fossa and strike your finger with the tendon hammer
How to ensure a reflex is in fact absent?from oxfordmedicaleducation.com
Ensure a reflex is in fact absent by reinforcing the reflex arc. To reinforce, ask the patient to clench their teeth or grasp hands together and pull apart just as you strike with the tendon hammer ( Jendrassik’s manoeuvre)
How many nerves are there in the brain?from hopkinsmedicine.org
Evaluation of the nerves of the brain. There are 12 main nerves of the brain, called the cranial nerves. During a complete neurological exam, most of these nerves are evaluated to help determine the functioning of the brain:
How many nerves are in the nervous system?from hopkinsmedicine.org
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, 12 nerves that come from the brain, and the nerves that come from the spinal cord. The circulation to the brain, arising from the arteries in the neck, is also frequently examined. In infants and younger children, a neurological exam includes the measurement of the head circumference.
Which nerve helps with the movement of the eyes?from hopkinsmedicine.org
The patient's healthcare provider may touch the face at different areas and watch the patient as he or she bites down. Cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve). This nerve helps with the movement of the eyes. The patient may be asked to follow a light or finger to move the eyes. Cranial nerve VII (facial nerve).